Key Takeaways
- Trust Wallet’s Chrome extension was compromised in a sophisticated attack that led to approximately $7 million in stolen crypto assets from 2,596 confirmed wallets.
- The attacker demonstrated “deep familiarity” with Trust Wallet’s source code, raising concerns about potential insider involvement according to cybersecurity firm SlowMist.
- While Trust Wallet received nearly 5,000 reimbursement claims (almost double the confirmed affected wallets), suggesting potential fraudulent claims attempting to exploit the reimbursement process.
- Binance co-founder Changpeng Zhao has pledged full coverage of legitimate losses, but the verification process presents significant challenges.
- The incident exposes a fundamental “structural tension” in self-custodial wallets: users control private keys but depend on centralized software that can be compromised.
The cryptocurrency industry faces yet another security breach, demonstrating that even established wallet providers aren’t immune to sophisticated attacks. This time, Trust Wallet—a popular self-custodial cryptocurrency wallet—has fallen victim, leaving thousands of users scrambling to secure their remaining assets while the company works to identify legitimate victims among a flood of claims.
The Christmas Day attack specifically targeted Trust Wallet’s Chrome browser extension, highlighting the particularly vulnerable nature of browser-based crypto tools. CertiK, a leading blockchain security firm, has called this incident “a stark reminder that convenience often comes with significant security tradeoffs in the cryptocurrency space” and emphasizes that users must understand these tradeoffs when choosing how to store their digital assets.
Trust Wallet Hack Exposes Major Security Flaw
The recent Trust Wallet breach has exposed a critical vulnerability in what many considered a relatively secure crypto storage solution. The hack specifically targeted version 2.68 of Trust Wallet’s Chrome extension, revealing how malicious code can be injected into trusted software update channels. This attack vector is particularly concerning because it bypassed traditional security measures like two-factor authentication and seed phrase protection by compromising the extension itself. What makes this breach particularly troubling is that it exploited what users typically consider a legitimate source—official browser extension updates—creating a scenario where even security-conscious users became vulnerable through no fault of their own.
How the $7M Trust Wallet Hack Happened
The Trust Wallet hack represents a sophisticated breach of a trusted cryptocurrency infrastructure component. Initial reports indicate the attack occurred on December 25, 2025, creating a particularly chaotic situation as many security teams operated with reduced holiday staffing. The timing appears deliberate, maximizing the window of opportunity before detection and intervention could occur.
Compromised Chrome Extension Vulnerability
According to cybersecurity researchers, the attack targeted a specific vulnerability in Trust Wallet’s Chrome extension update mechanism. Version 2.68 of the extension contained malicious code that, once installed by users, could extract private keys and seed phrases. The code was sophisticated enough to operate silently in the background while appearing to function normally to users. Once compromised, the extension transmitted sensitive wallet information to attacker-controlled servers, allowing them to drain funds from affected wallets almost instantaneously. This approach demonstrates how centralized update mechanisms can become critical points of failure even in ostensibly decentralized systems.
Attacker’s “Deep Familiarity” With Source Code
Perhaps most concerning about this breach is cybersecurity firm SlowMist’s assessment that the attacker demonstrated “deep familiarity with Trust Wallet’s source code.” This technical insight suggests the possibility of insider knowledge or extensive reconnaissance of Trust Wallet’s systems. The malicious code was implemented with precision, targeting specific functions within the extension while avoiding detection mechanisms. According to SlowMist’s analysis, the attack required not just technical prowess but intimate understanding of Trust Wallet’s extension architecture and security protocols. This incident echoes other alarming security breaches, such as the Joburg water contamination alert, highlighting vulnerabilities in critical systems.
The carefully crafted exploit managed to bypass multiple security layers that would typically flag suspicious code in an update. This suggests either a sophisticated supply chain attack or potentially compromised development infrastructure. The attack’s technical sophistication has prompted Trust Wallet to engage multiple external security firms to conduct comprehensive forensic investigations.
Timeline of the Christmas Day Attack
The Trust Wallet hack unfolded with alarming speed once initiated. Users first reported unusual transaction activity early on December 25th, with unexplained outgoing transfers appearing across multiple blockchains. By midday, social media channels were flooded with reports of unauthorized transactions, prompting Trust Wallet’s security team to investigate. The company identified the compromised extension by evening and immediately advised all users to disconnect it from their browsers.
Trust Wallet officially acknowledged the breach via Twitter approximately 12 hours after the first reported incidents, warning users to cease using the Chrome extension immediately. Within 24 hours of the initial attack, security researchers had confirmed that approximately $7 million in various cryptocurrencies had been extracted from user wallets. The rapid evolution of this attack demonstrates why immediate response and transparency are crucial in crypto security incidents.
The True Scope of the Breach
While initial reports focused on the $7 million figure, security experts caution that understanding the true impact requires looking beyond raw financial totals. The breach affects thousands of individual users, many of whom may have lost significant portions of their crypto holdings. Beyond immediate financial losses, the incident has damaged user trust in browser-based wallet extensions more broadly and raised questions about the security model of web3 infrastructure components.
The long-term consequences extend beyond direct losses, as affected users must now deal with tax implications of stolen assets, potential identity concerns if personal information was compromised, and the psychological impact of experiencing a security breach. For many, this incident represents their first direct exposure to cryptocurrency security failures, potentially influencing their future participation in the ecosystem.
2,596 Confirmed Wallet Addresses Affected
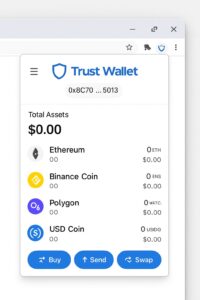
Trust Wallet CEO Eowyn Chen has confirmed that exactly 2,596 wallet addresses have been identified as victims of the breach. These addresses were specifically linked to users who had installed the compromised Chrome extension version 2.68 and had actively used it to manage their cryptocurrencies. The affected wallets span multiple blockchain networks, including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and several other popular chains where Trust Wallet offers support. This multi-chain impact significantly complicates both the forensic investigation and reimbursement processes.
Security researchers have observed that the attack disproportionately affected wallets with higher balances, suggesting the hackers may have prioritized larger holdings when executing their theft. On-chain analysis indicates that approximately 60% of the stolen value came from just 15% of the compromised wallets. This targeting pattern implies sophisticated selection criteria beyond simple automation, potentially indicating manual selection of high-value targets after the initial compromise.
Nearly 5,000 Reimbursement Claims Filed
In an unexpected development that has complicated the recovery process, Trust Wallet has received nearly 5,000 reimbursement claims—almost double the number of confirmed affected wallets. This discrepancy has forced the company to implement a rigorous verification protocol to distinguish legitimate victims from opportunistic false claims. The verification team must now analyze transaction histories, login patterns, and other technical indicators to validate each claim individually.
The surge in potentially fraudulent claims highlights a common challenge following high-profile crypto breaches: secondary exploitation attempts targeting the reimbursement process itself. Trust Wallet has brought in specialized forensic accountants with blockchain expertise to help filter legitimate claims from opportunistic ones, but this additional layer of verification will inevitably delay the reimbursement timeline for genuine victims.
Types of Crypto Assets Stolen
The $7 million stolen represents a diverse portfolio of cryptocurrency assets. According to blockchain analytics firm Elliptic, approximately 40% of the stolen funds were in Ethereum and ERC-20 tokens, 30% in BNB Chain assets, 15% in Polygon-based tokens, and the remaining 15% distributed across various other chains including Solana, Avalanche, and Arbitrum. The hackers showed particular interest in stablecoins like USDT and USDC, which accounted for roughly 35% of the total value taken, likely due to their ease of liquidation and stable value.
“What’s particularly concerning about this attack is its cross-chain nature. The attacker demonstrated sophisticated capabilities to extract and move assets across multiple blockchains simultaneously, suggesting this wasn’t an opportunistic hack but a carefully orchestrated operation.” — Cybersecurity firm SlowMist
Trust Wallet’s Response and Recovery Plan
Trust Wallet’s response to the breach has been multi-faceted, combining immediate containment measures with longer-term recovery planning. Within hours of confirming the breach, the company disabled the compromised extension version, pushed emergency notifications to mobile app users, and established dedicated communication channels for affected users. This rapid response likely prevented additional losses, though critics argue the company could have detected the compromised extension earlier through more rigorous security monitoring.
The company has also assembled a cross-functional incident response team incorporating internal security experts alongside external consultants from firms specializing in blockchain forensics. This team is working on both tracking the stolen funds across various blockchains and implementing enhanced security measures for future extension updates. Their technical findings will reportedly be published in a comprehensive post-mortem once the immediate recovery efforts are complete.
Binance Co-Founder Pledges Full Coverage of Losses
In a significant development that has provided some reassurance to affected users, Binance co-founder Changpeng “CZ” Zhao has publicly committed to ensuring all legitimate victims receive full compensation for their losses. This pledge carries substantial weight given Binance’s acquisition of Trust Wallet in 2018 and the company’s significant financial resources. CZ emphasized that “user security remains our absolute priority” in his statement addressing the incident.
The reimbursement program will reportedly cover verified losses at the USD value at the time of the theft, though specific implementation details are still being finalized. This approach aligns with industry best practices established following previous high-profile crypto breaches. However, users should be aware that reimbursement may take several weeks as the verification process unfolds and the full scope of legitimate claims becomes clear.
Verification Process for Legitimate Claims
Trust Wallet has implemented a multi-stage verification process for users claiming losses from the breach. The process begins with claimants submitting wallet addresses, transaction hashes showing the unauthorized transfers, and timestamps of when they installed the compromised extension. This initial data is then cross-referenced against internal logs and blockchain data to confirm the claim’s legitimacy. Users whose claims pass this preliminary verification are then required to complete additional identity verification steps before final approval for reimbursement.
The verification team is prioritizing claims based on a combination of factors, including submission time, clarity of documentation, and evidence quality. This triage approach aims to process the most clearly legitimate claims first while allocating additional resources to cases requiring deeper investigation. Trust Wallet has not provided a specific timeline for completing all verifications, acknowledging that more complex cases may require several weeks of forensic analysis.
Forensic Investigation Status
The forensic investigation into the Trust Wallet breach is ongoing, with multiple security firms contributing specialized expertise. Investigators have already established that the attack originated from a sophisticated compromise of Trust Wallet’s extension update infrastructure rather than individual account takeovers. On-chain analysis has identified several cryptocurrency mixing services being used to launder the stolen funds, complicating recovery efforts but providing valuable intelligence on the attackers’ methods. The incident has prompted probes into intelligence lapses similar to those seen in other high-profile cases.
Initial findings suggest the attacker may have gained access to private keys through a combination of code injection and credential interception techniques. Security researchers have noted that the malicious code was designed to evade standard security scans by mimicking legitimate functionality while secretly extracting sensitive information. The investigation continues to explore how the attackers initially gained access to Trust Wallet’s update infrastructure, with particular focus on potential supply chain vulnerabilities or insider threats.
Red Flags That Suggest Possible Inside Job
Several unusual aspects of the Trust Wallet breach have led security experts to consider the possibility of insider involvement or access. The highly targeted nature of the attack, the sophisticated implementation that evaded detection systems, and the attacker’s apparent familiarity with Trust Wallet’s internal architecture all raise concerns about potential insider knowledge. While investigations remain ongoing and no definitive conclusions have been reached, these red flags have prompted additional scrutiny of internal access controls and development processes.
Access to Update Mechanisms
One particularly troubling aspect of the Trust Wallet hack is the attackers’ access to code signing and update distribution systems. These systems typically employ rigorous security measures and multi-person authorization protocols. The fact that attackers could inject malicious code into an official release suggests either a sophisticated breach of these systems or potential insider access. Trust Wallet’s security team is conducting a comprehensive audit of their code review and deployment processes, with special attention to access logs and authorization records from the weeks leading up to the breach. In a related event, the UK probes intelligence lapses in a high-profile case, highlighting the importance of robust security protocols.
SlowMist Security Analysis Findings
Respected blockchain security firm SlowMist’s analysis of the compromised extension revealed sophisticated techniques that required extensive knowledge of Trust Wallet’s architecture. According to their preliminary report, “The malicious code was inserted with surgical precision into specific components where it would be least likely to trigger security alerts or cause noticeable performance issues.” SlowMist researchers noted that the code appeared tailored to Trust Wallet’s unique implementation rather than utilizing generic wallet-draining techniques, suggesting the attackers had studied the codebase extensively or possibly had prior access to it.
SlowMist’s analysis also indicated that the attackers employed techniques to avoid detection even after installation, including delayed execution and conditional triggering based on wallet balances. These sophisticated evasion techniques bear hallmarks of advanced persistent threats rather than opportunistic hackers, raising the stakes of the investigation significantly.
Self-Custodial Wallet “Structural Tension” Problem
The Trust Wallet breach illuminates what industry experts call the “structural tension” inherent in many self-custodial wallet solutions. While these wallets offer users control over their private keys—a fundamental principle in cryptocurrency—they still rely on centralized software development, distribution, and update mechanisms. This creates an inherent contradiction: users believe they have full self-custody, but their assets remain vulnerable to compromises in the centralized infrastructure supporting their supposedly decentralized wallet.
This structural weakness isn’t unique to Trust Wallet but represents a broader challenge for the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem. As wallets strive to become more user-friendly and feature-rich, they inevitably introduce additional components and dependencies that expand the potential attack surface. The industry faces a fundamental design challenge in balancing security, decentralization, and usability—a challenge thrown into sharp relief by this recent breach.
Private Key Control vs. Centralized Dependencies
At the heart of the “structural tension” problem lies the disconnect between theoretical and practical self-custody. While Trust Wallet users control their private keys in principle, the Chrome extension that interfaces with these keys introduced a fatal centralized dependency. When that extension was compromised, the private key control became effectively meaningless. This contradiction challenges the fundamental value proposition of many self-custodial wallets that promise users complete control while maintaining centralized update channels that can potentially undermine that control.
The breach demonstrates that security must be evaluated across the entire system, not just at the level of key storage. Even if private keys are never directly stored by the wallet provider, the software that allows users to generate and interact with those keys represents a critical vulnerability if compromised. This realization is prompting renewed interest in open-source wallet solutions with transparent, community-verified code and minimal update requirements.
Software Update Security Risks
The Trust Wallet incident highlights the particular vulnerability introduced by automatic software updates—a standard feature in most modern applications designed to improve security by ensuring users have the latest patches. Ironically, this security-focused feature became the attack vector that enabled the theft. The trusted update channel allowed attackers to distribute malicious code under the guise of legitimate software improvements, bypassing users’ natural skepticism and security awareness.
This update-based attack vector is especially concerning because it exploits a fundamental trust relationship between users and software providers. When users authorize an application to automatically update, they’re extending significant trust to the developer’s ability to maintain secure deployment pipelines. The Trust Wallet breach has prompted calls for more transparent update verification processes, including optional manual review of significant changes and clearer communication around update contents. In the wake of such incidents, it’s crucial to stay informed about potential security risks, such as the recent Joburg water contamination alert, which highlights the importance of vigilance in various sectors.
How to Check If Your Trust Wallet Was Compromised
For users concerned about potential compromise, Trust Wallet has established a verification portal where users can check if their wallet addresses appear on the confirmed list of affected accounts. This self-service tool requires entering wallet addresses to determine if they were among the 2,596 wallets identified as compromised. Additionally, users should review their transaction history for any unauthorized transfers that occurred between December 24-26, paying special attention to transactions they don’t recognize that moved assets to unfamiliar addresses.
If you suspect your wallet may have been affected but haven’t received confirmation, Trust Wallet recommends proactively submitting information through their designated claim portal while continuing to monitor for unusual activity. The company has also established a dedicated support channel specifically for breach-related inquiries, staffed by specialists familiar with the incident details and verification requirements.
Identifying Suspicious Transactions
Suspicious transactions typically share several common characteristics that can help users identify potential unauthorized transfers. These often include transfers to previously unused addresses, movements of entire wallet balances (rather than specific amounts), and transactions occurring at unusual times or in rapid succession. Trust Wallet recommends reviewing transactions across all networks you’ve used with your wallet, as the attack affected multiple blockchains simultaneously.
Blockchain explorers like Etherscan, BscScan, and similar tools for other networks provide detailed transaction histories that can help identify unauthorized transfers. Users should pay particular attention to transactions initiated during the December 25th period when the attack was most active. In some cases, attackers attempted to disguise their transfers by breaking them into multiple smaller transactions, so users should watch for unusual patterns of consecutive outgoing transfers.
Steps to Submit a Legitimate Claim
Trust Wallet has established a structured process for submitting theft claims related to this breach. The process begins with the dedicated claim form available on their official website, which requires detailed information about affected wallets and lost assets. Users must provide wallet addresses, approximate loss amounts, and timestamps of unauthorized transactions. Additionally, claimants need to demonstrate ownership of the affected wallet through a verification transaction or signed message from a known secure device. For more information on similar incidents, you can read about the Coral Adventurer cruise ship grounding incident in Papua New Guinea.
Once submitted, claims enter a queue for verification by the Trust Wallet security team. The company recommends retaining all relevant evidence of the compromise, including screenshots of transaction histories and any communication received from Trust Wallet around the time of the breach. Users who have already submitted claims can check their status through a dedicated portal using their claim reference number.
Documentation You’ll Need
Preparing thorough documentation significantly improves the chances of successful claim verification. At minimum, affected users should compile transaction hashes of unauthorized transfers, screenshots of their wallet before and after the incident if available, and any evidence showing they were using the compromised extension version. Additional helpful documentation includes records of when the extension was installed or updated, any error messages or unusual behaviors noticed before the theft, and timestamps of when unusual activity was first detected.
Trust Wallet also requests proof of ownership documentation, which may include previous transaction history showing regular usage patterns, purchase records for acquired cryptocurrencies, or other evidence establishing legitimate ownership prior to the breach. Users with significant losses may be asked to provide additional verification during the claims process, potentially including video verification or notarized statements depending on the claim amount. For more details on how Trust Wallet is handling these claims, you can read about the thousands of false claims flagged after the hack.
Immediate Steps to Secure Your Crypto Assets
If you suspect your Trust Wallet may have been compromised—or even if you’re just concerned about potential vulnerability—immediate action is essential to protect any remaining assets. First and most urgently, transfer any remaining funds to a completely different wallet solution from another provider, preferably one that uses different seed phrases and security architecture. This transfer should be done from a secure device that has never had the compromised extension installed to prevent potential keylogging or further interception.
Next, uninstall not just the Trust Wallet extension but any browser extensions that have access to sensitive information or financial accounts, as a precautionary measure. Perform a thorough security scan of your device using reputable antimalware software to identify any potential remaining threats. Finally, reset passwords for any cryptocurrency exchanges or services accessed from the same device, preferably from a different secure device after completing malware scans.
Remove Compromised Extensions
Completely removing the compromised Trust Wallet extension requires more than just the standard uninstall process. Users should first disconnect the extension from any connected websites through the extension settings, then uninstall it through the browser’s extension management page. After uninstallation, clear browser cache, cookies, and local storage to remove any potentially persistent malicious code. For maximum security, consider reinstalling your browser completely or using browser reset functions to ensure no traces of the compromised extension remain. For more insights into digital security, you might find this article on intelligence lapses relevant.
Transfer Funds to Secure Wallets
When moving funds to a new secure wallet, choose your destination carefully. Hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor offer significant security advantages over software solutions, as they store private keys on dedicated devices with limited attack surfaces. If you don’t have immediate access to a hardware wallet, consider using a newly installed mobile wallet from a reputable provider as a temporary measure until a more secure long-term solution can be implemented. Prioritize moving the largest value assets first if you’re racing against potential attackers who may still have access to your wallet.
During the transfer process, verify receiving addresses multiple times before confirming transactions. If possible, start with a small test transaction to confirm everything works correctly before moving larger amounts. Remember that different blockchains require different approaches, so methodically work through each cryptocurrency type in your compromised wallet.
Enable Additional Security Features
On your new wallet, immediately implement all available security features before receiving significant funds. This includes enabling any available two-factor authentication, biometric verification, transaction confirmations, and spending limits. If your new wallet supports whitelisting addresses, configure this feature to restrict transfers to only known and verified receiving addresses. For hardware wallets, enable PIN protection and passphrase features that provide additional security layers beyond the standard recovery seed.
Report Unauthorized Transactions
Reporting unauthorized transactions serves both to support your reimbursement claim and to help the broader investigation. Document and report theft details to Trust Wallet’s incident response team, providing transaction hashes, timestamps, and destination addresses where your funds were sent. Additionally, consider filing reports with relevant law enforcement agencies, as cryptocurrency thefts increasingly fall under cybercrime jurisdictions in many countries. For significant losses, consulting with an attorney specializing in cryptocurrency matters can provide guidance on potential recovery options beyond the Trust Wallet reimbursement process.
Better Alternatives to Protect Your Crypto
The Trust Wallet breach serves as a painful reminder that cryptocurrency security requires a layered approach that doesn’t rely exclusively on any single solution. Even reputable wallet providers can experience security failures, making a diversified security strategy essential for serious crypto investors. This approach should combine technological solutions with behavioral security practices, creating multiple layers that an attacker would need to breach.
While no solution offers perfect security, certain approaches significantly reduce risk compared to browser-based extensions. The primary consideration should be minimizing attack surface—the fewer systems and code paths that handle your private keys, the fewer opportunities exist for compromise. This principle favors simpler, focused solutions over feature-rich applications that may introduce additional vulnerabilities through complexity.
When evaluating alternative wallet solutions, consider not just the security features advertised but also the provider’s security track record, transparency about previous incidents, and response capabilities. A wallet with slightly fewer convenience features but stronger security foundations and a responsive security team typically represents the better choice for storing significant assets. For instance, understanding how organizations handle incidents, such as the Coral Adventurer cruise ship grounding incident, can provide insights into their crisis management capabilities.
Hardware Wallets vs. Software Wallets
Hardware wallets represent the gold standard for cryptocurrency security by keeping private keys on specialized devices that never directly connect to the internet. These physical devices require manual confirmation of transactions through button presses or screen interactions, making remote exploitation extremely difficult compared to software-only solutions. Leading options like Ledger, Trezor, and KeepKey offer varying features and supported cryptocurrencies, but all provide substantial security improvements over browser extensions or mobile apps.
The primary security advantage of hardware wallets comes from their air-gapped design—private keys remain on the device and transactions must be physically confirmed, making remote exploitation nearly impossible without physical access to the device. While software wallets store keys on general-purpose devices exposed to multiple applications and potential malware, hardware wallets isolate keys on devices purpose-built for security. This fundamental architectural difference explains why hardware wallets remain the recommended solution for storing significant cryptocurrency holdings despite their higher cost and slightly reduced convenience.
Multi-Signature Security Options
Multi-signature (multisig) wallets provide enhanced security by requiring multiple separate keys to authorize transactions, similar to requiring multiple signatures on high-value checks. This approach means that even if one key or device is compromised, funds remain secure as long as the attacker cannot access the additional required keys. Multisig solutions like Gnosis Safe, Casa, and Electrum’s multisig feature allow users to create wallets requiring 2-of-3, 3-of-5, or other key combinations, distributing security risk across multiple devices or individuals.
Cold Storage Solutions
Cold storage represents the most conservative approach to cryptocurrency security, keeping private keys entirely offline and disconnected from any networked device. Beyond hardware wallets, true cold storage might include paper wallets generated on air-gapped computers, metal seed phrase backups stored in secure locations, or specialized vault services offered by institutional custodians. While these methods sacrifice convenience for security, they remain the preferred approach for long-term storage of significant holdings that don’t require frequent access or trading.
Lessons Every Crypto Investor Must Learn From This Breach
The Trust Wallet breach reinforces several fundamental lessons that every cryptocurrency investor should internalize. First, security and convenience inevitably involve tradeoffs—features that make wallets easier to use often introduce additional attack vectors. Second, diversification applies not just to investment portfolios but also to security approaches—storing all assets in a single wallet creates unnecessary concentration risk regardless of the provider’s reputation. Third, automatic updates represent both security benefits and potential risks, suggesting users should consider manual update approval for critical financial applications. Finally, even self-custodial solutions can harbor centralized vulnerabilities, making it essential to understand the complete security model of any wallet solution rather than relying on marketing claims about “self-custody” or “decentralization.”
Frequently Asked Questions
In the aftermath of the Trust Wallet breach, users have raised numerous important questions about implications, responsibilities, and next steps. The following FAQs address the most common concerns based on official statements from Trust Wallet and analysis from security experts. These answers reflect the most current information available, though users should continue monitoring Trust Wallet’s official channels for updates as the situation evolves.
For technical assistance with specific claims or security concerns not addressed here, users should contact Trust Wallet’s dedicated incident response team through official support channels rather than relying on general guidance. The company has established specialized support teams focused exclusively on breach-related inquiries to provide more targeted assistance than their general customer service.
Remember that in matters of cryptocurrency security, information from unofficial sources should be treated with skepticism, as misinformation and scams often proliferate following high-profile security incidents. Verify all recommendations through multiple trusted sources before taking action that affects your assets.
- Verify all information through Trust Wallet’s official channels, not social media or messaging apps
- Never share your seed phrase or private keys, even with people claiming to be from support
- Be skeptical of “recovery services” that emerge after breaches—these are typically scams
- Document everything related to unauthorized transactions for potential legal or insurance purposes
- Consider consulting with a cryptocurrency security specialist for significant losses
Will Trust Wallet reimburse all affected users?
Trust Wallet has committed to reimbursing all users with verified legitimate claims, with Binance co-founder CZ publicly backing this commitment. However, reimbursement is contingent on successful verification through their claims process, which requires demonstrating that losses directly resulted from the compromised Chrome extension rather than other security issues. Users with wallets confirmed on the official list of 2,596 affected addresses should expect full compensation, while those making claims outside this list face a more rigorous verification process with no guarantee of approval.
How do I know if my Trust Wallet extension is vulnerable?
All versions of the Trust Wallet Chrome extension should be considered potentially vulnerable until further notice. Trust Wallet has specifically identified version 2.68 as the compromised version, but as a precautionary measure, they’ve recommended complete removal of all versions pending a comprehensive security audit and rebuild. Users can check their extension version in Chrome’s extension management page, but the safest approach is complete removal regardless of version. For more information on security incidents, you can read about the Coral Adventurer cruise ship grounding incident.
Trust Wallet has temporarily halted all extension updates while they implement enhanced security measures in their development and deployment pipelines. The company has indicated they will release a completely rebuilt extension with additional security protections once their investigation concludes, but no specific timeline has been provided for this release.
Can I still use Trust Wallet mobile app safely?
According to Trust Wallet’s security team, the mobile applications for iOS and Android were not affected by the same vulnerability that compromised the Chrome extension. The company has stated that their investigation has found no evidence of compromise in the mobile application codebase or distribution channels. However, as a precautionary measure, they recommend users update to the latest version of the mobile application, which contains additional security enhancements implemented in response to the breach.
What happens if my claim is rejected by Trust Wallet?
If your reimbursement claim is rejected, Trust Wallet provides an appeals process where you can submit additional evidence supporting your case. Rejected claimants receive detailed explanations of why their claims were denied and specific guidance on what additional information might help overturn the decision. For claims rejected due to insufficient evidence rather than suspected fraud, the appeals process has been successful in approximately 30% of cases where users provided additional documentation or clarification. For more information, you can read about how Trust Wallet flags thousands of false claims after a major security incident.
How long will the verification and reimbursement process take?
Trust Wallet has indicated that the verification process for straightforward claims typically takes 2-3 weeks from submission to decision, with reimbursement following within 7-10 days of approval. More complex cases requiring additional investigation may take longer, particularly for large amounts or claims with unusual circumstances. The company is processing claims in batches, prioritizing clearly legitimate cases associated with wallets on their confirmed affected list. Users can check their claim status through the dedicated portal using their claim reference number, with updates typically provided at least weekly during the verification process.
This timeline represents Trust Wallet’s current estimates based on processing the first wave of claims, but they’ve acknowledged that the verification process may extend longer as they work through more complex cases. The company has expanded their verification team to accelerate processing while maintaining thorough security checks to prevent fraudulent claims from being approved.
For investors concerned about future security, Bitpanda offers industry-leading security protocols that protect your digital assets with military-grade encryption and cold storage technology, helping you avoid the vulnerabilities exposed in the Trust Wallet breach.
The recent theft of $7 million from Trust Wallet users has raised significant concerns in the crypto community. A total of 2,596 wallets were affected, highlighting the vulnerabilities in digital asset security. This incident is reminiscent of other recent events that have put a spotlight on security lapses, such as the UK’s probe into intelligence lapses in the case of a British-Egyptian activist. As the investigation continues, users are urged to take extra precautions to safeguard their assets.